1. Polarization Measuring Instrument
In the previous several articles, we have made a systematic introduction to the commonly used polarized optical elements. According to different functions, polarized optical elements can be divided into polarizer, retarder, compensator and depolarizer four categories. For these polarizing elements, it is necessary to have appropriate detection instruments to test their polarization performance. Take the common 1/4 wave plate as an example, its theoretical phase delay is 90 degrees, then for the actual production of wave plate products, its phase delay is exactly how much, a polarization meter is needed to test this parameter. Polarimeter is a kind of equipment which can measure the polarization parameters of samples. It can collect and analyze the light intensity through the sample or reflected by the sample. In the field of optical elements, polarizers are often used to measure the stress birefringence, dichroism and scattering properties of optical materials or elements. Ellipsometry is a special polarization measuring instrument, which is used to measure and characterize thin films and optical surfaces. It can measure the refractive index, thickness and extinction coefficient of the substrate and each layer. Because the light after passing through the sample is usually elliptically polarized, it is called ellipsometer. In order to obtain reliable test results, it is usually necessary to test multiple incident angles at multiple wavelengths. This kind of multi-wavelength instrument is also called spectral ellipsometer. A common polarizer is usually composed of a light source, a polarizer, a measured sample, a polarizer and a detector, thus, the parameter indexes to be measured are obtained. For specific applications, the polarizer also includes the compensator (variable retarder) we described earlier to test the azimuth of the sample. Polarizer (p) , Sample (s) , Compensators (C) , Polarizer (Analyzer) , Polarizer (a) , Compensators (c) , Polarizer (a) , Polarizer (a) , Compensators (c) , Polarizer (a) , Compensators (a) , Polarizer (a) , Compensators (c) , Polarizer (a) , Compensators (a) , Compensators (a) , Compensators (a) , Compensators (a) , Compensators (a) , Compensators (a) , Compensators (a) According to the need of practical test, polarization measurement instrument can be divided into three types: PSA, PCSA and PCSCA.
2. PSA
The PSA form is the basic structure of polarimeter. The non-polarized light from the light source is received by the light intensity detector after passing through the polarizer, sample and polarizer. In order to test the polarization parameters of the sample, there are various deformations in the PSA structure form. For example, the polarizer is rotating while the sample and the polarizer are fixed, as follows:
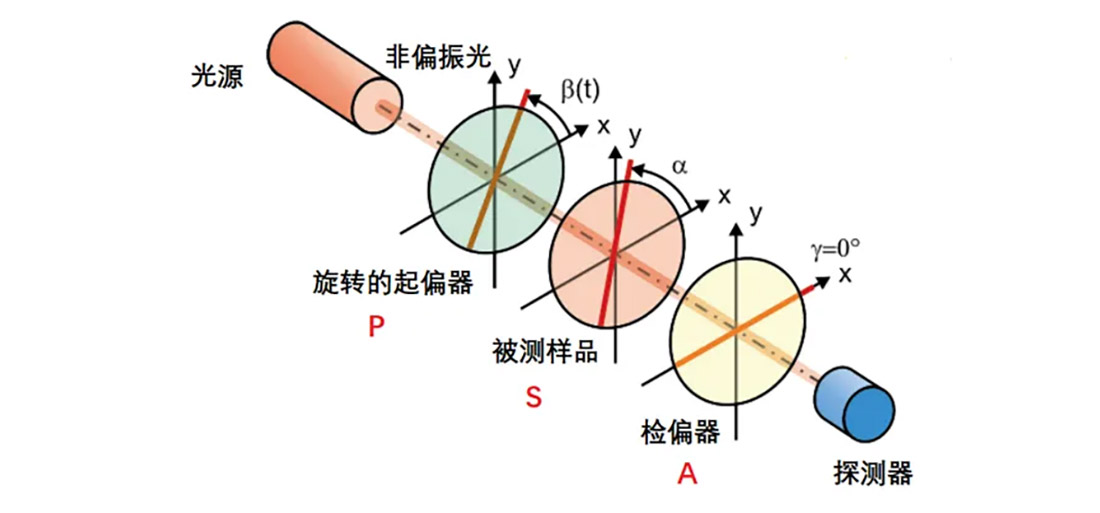
In the above image, by rotating the polarizer, the light incident on the sample is linearly polarized light with a regular change in the polarization direction. The Jonnes matrix, which contains the polarization information of the sample, can be calculated to complete the test. In other test cases, the polarizer and detector can be set to be fixed, the sample rotates at a certain speed, or the sample can be fixed, the polarizer and the detector rotate at a certain rate, and a variety of polarization information of the sample can be obtained by calculation.
3. PCSA
In contrast to the PSA form, the PCSA structure incorporates a compensator between the polarizer and the sample under test. We know that the compensator is a delay whose phase delay can vary over a range, it is equivalent to adding more parameters into the test optical path, so that more polarization information of the sample can be tested. Sometimes the compensator can be replaced by a wave plate with a fixed delay. The commonly used ellipsometer uses this kind of structure, its principle is as follows:
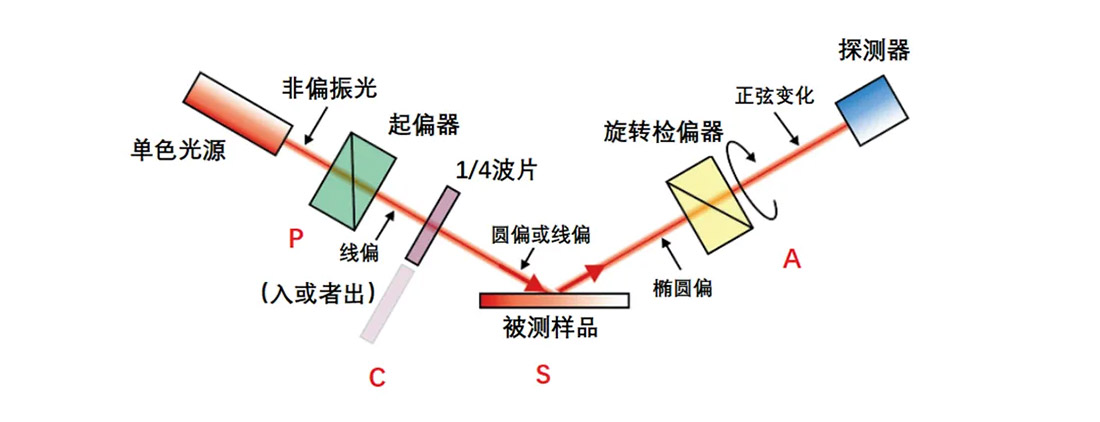
In the ellipsometer light path shown above, the polarizer is fixed and the angle of the polarizer is 45 ° . A 1/4 wave plate is between the polarizer and the sample. It can be inserted into or pulled out of the optical path. A circularly or linearly polarized beam is reflected by the sample and becomes an elliptically polarized light, the light beam passing through the rotating polarizer can form a sinusoidal light spot at the detector end. In some cases, the compensator is placed between the measured sample and the polarizer, forming a PSCA structure that functions similarly. The variation of polarization state of reflected and transmitted light can be measured by ellipsometer, and the amplitude attenuation ratio and phase difference of reflected light p-wave and s-wave can be described by ψ and δ respectively, combined with known input values, the ellipsometer can accurately calculate the sample parameters, which is a non-destructive, non-contact film thickness, optical characteristics of the detection technology.
4. PCSCA
In order to obtain more complete and accurate information of the detected samples, a polarization measuring instrument with PCSCA structure is developed, which consists of two compensators, the first of which is located between the polarizer and the measured sample, the second compensator is located between the measured sample and the polarizer, as shown in the following figure:
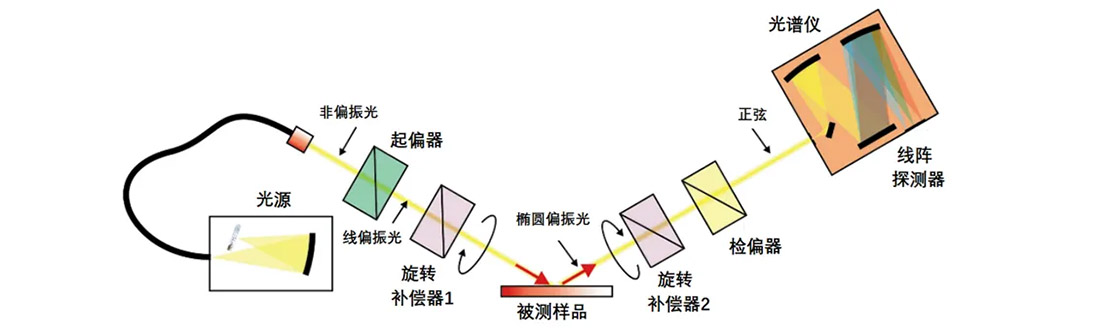
Because the main function of ellipsometry is to test and characterize the films, it is necessary to analyze the refractive index n and dielectric coefficient K of the materials at different wavelengths. In the ellipsometer above, a wide-band white light source is used. The non-polarized light from the source passes through the polarizer and becomes linearly polarized light, after passing through the first rotating compensator, the measured sample and the second rotating compensator, the linearly polarized light is detected by a polarizer and becomes a sinusoidal light beam, it is widely used in semiconductor film or metal film for its high speed and high precision, and it can be used to measure the polarization characteristics of multi-wavelength channels.